Chinese Scientists Use Remote Sensing Technology to Digitize Great Wall
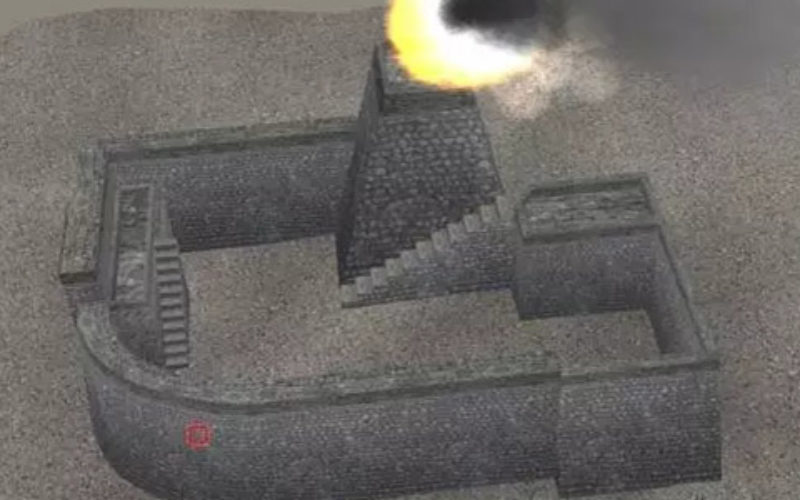

Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently used remote-sensing equipment in their efforts to restore a vanished section of the Great Wall in Northwest China’s Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region.
By analyzing the local conditions of the landscape with remote sensing technology, the researchers were able to recreate a digital model of the Great Wall.

China Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth (RADI) under the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS)
This section of the Great Wall was built nearly 1,000 years ago to protect Xinjiang from invaders, but was gradually eroded over the centuries by wind and sand.
Similar to radar, remote-sensing technology used in archeology makes use of electromagnetic waves to detect and observe relics located underground.
“Different from other areas of China, the Great Wall in Xinjiang didn’t have connected high walls but were separate fortresses located at main roads and passes and along river banks,” CAS researcher Nie Yueping told the People’s Daily.
So far, more than 600 locations making up the Xinjiang Great Wall have been discovered.
Source: Chinese Academy of Sciences