About GLONASS


What is GLONASS?
GLONASS(GLObal’naya NAvigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema; “GLObal NAvigation Satellite System” in English) is a radio-based satellite navigation system, developed by the former Soviet Union and now operated for the Russian government by the Russian Space Forces. It is an alternative and complementary to the United States’ Global Positioning System (GPS), the Chinese COMPASS Navigation System, and the planned Galileo positioning system of the European Union (EU).
Development began in 1976, with a goal of global coverage by 1991. Beginning on 12 October 1982, numerous rocket launches added satellites to the system until the constellation was completed in 1995. Following completion, the system rapidly fell into disrepair with the collapse of the Russian economy. Beginning in 2001, Russia committed to restoring the system, and in recent years has diversified, introducing the Indian government as a partner, and accelerated the program with a goal of restoring global coverage by 2009.
Purpose of GLONASS
GLONASS was developed to provide real-time position and velocity determination, initially for use by the Soviet military for navigation and ballistic missile targeting. It was the Soviet Union’s second generation satellite navigation system, improving on the Tsikada system which required one to two hours of signal processing to calculate a location with high accuracy. By contrast, once a receiver is tracking the satellite signals, a position fix is available instantly. It is stated that at peak efficiency the system’s standard positioning and timing service provide horizontal positioning accuracy within 57–70 meters, vertical positioning within 70 meters, velocity vector measuring within 15 cm/s, and time transfer within 1 µs (all within 99.7% probability).
Throughout this federal program the following results were achieved:
- The GLONASS system was preserved, modernized and became operational consisting of “GLONASS-K” satellites. Nowadays there are two existing operational global navigation satellite systems: GPS and GLONASS
- Ground control segment was modernized that together with the orbital constellation ensures the accuracy characteristics at a level commensurate with those of GPS
- The State Standard of time and frequency facilities and the Earth rotation parameters definition facilities were modernized
- GNSS augmentation prototypes, great amount of patterns of core receiving and measuring modules, continuous positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) equipment for civil and special use and related systems were designed.
Nowadays, GNSS technologies are used in a growing number of applications. To suit user needs, the GLONASS system, as well as user navigation devices, must be continually improved. First and foremost, it applies to high precision applications that require real-time accuracy of a decimeter or a centimetre. It also applies to applications that deal with security.
Since 2012, the system has been evolving in the direction of efficient continuous positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) task solving for the benefit of the country’s military, security, and long-term social and economic growth.
The following factors are taken into account by the new federal programme :
- Support with guaranteed competitive performance
- Development aiming at attaining parity with international navigation satellite systems and Russian Federation leadership in satellite navigation
- Use both on Russian Federation territory and overseas
The GLONASS system’s evolution for the benefit of increasing user requirements and competitiveness is largely governed by the space segment’s capabilities. Capability enhancements through satellites generations are listed in the table below.
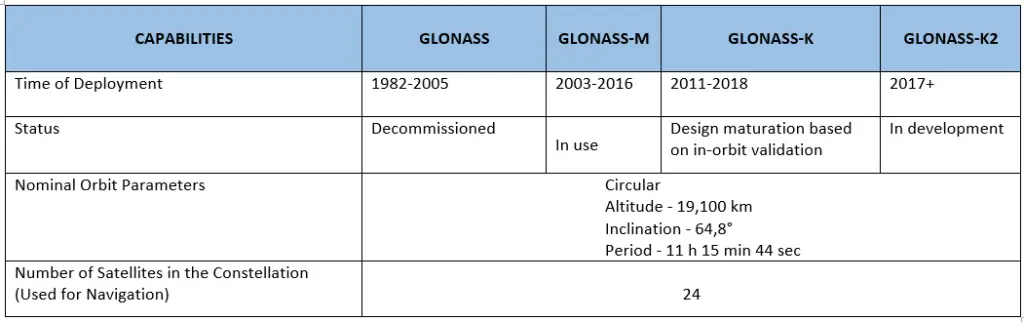
Source – GLONASS History
Also Read –



