Utility Data 101: Understanding the Basics of Infrastructure Information
Are you eager to explore the essentials of infrastructure information? Look no further than ‘Utility Data 101: Understanding the Basics of Infrastructure Information.’ This comprehensive guide is designed to help you grasp the importance of utility data and navigate the intricacies of managing and analyzing this valuable resource. From the types of infrastructure information to the challenges you may encounter, this informative resource covers it all. Discover the future trends in infrastructure information and gain the knowledge you need to make informed decisions. So, get ready to dive into the world of utility data and unlock the potential it holds for your organization.
Importance of Utility Data
Understanding the importance of utility coordination is crucial for anyone involved in managing infrastructure systems. Utility data refers to the information collected and analyzed from various utility systems, such as electricity, water, gas, and telecommunications. This data provides valuable insights into the performance, efficiency, and maintenance needs of these systems.
One of the key reasons why utility data is essential is its role in decision-making. By analyzing this data, managers can identify patterns, trends, and anomalies within the infrastructure systems. This information is vital for making informed decisions regarding maintenance, upgrades, and resource allocation. Without access to accurate and up-to-date utility data, managers would be operating blindly, leading to potential inefficiencies and costly mistakes.
Moreover, utility data is also critical for ensuring regulatory compliance. Many infrastructure systems are subject to strict regulations and standards. By regularly monitoring and analyzing utility data, managers can ensure that their systems meet these requirements. Failure to comply with regulations can result in penalties, legal issues, and potentially jeopardize the safety and reliability of the infrastructure.
Types of Infrastructure Information
To understand the types of infrastructure information, you need to know the various categories in which this data is classified. Infrastructure information can be broadly categorized into three main types: physical, operational, and spatial data. Physical data refers to information about the physical assets of utility systems, such as pipelines, power lines, and water treatment plants. This data includes details about the location, condition, and capacity of these assets.
Operational data, on the other hand, focuses on the functioning and performance of utility systems. It includes data on energy production and consumption, water usage, and system reliability. This information is crucial for monitoring and optimizing the operations of utility systems.
Lastly, spatial data provides the geographical context for infrastructure information. It includes maps, satellite imagery, and GIS (Geographic Information System) data. Spatial data helps utility companies visualize and analyze the physical layout of their assets and understand their relationship with the surrounding environment.
Collecting and Analyzing Utility Data
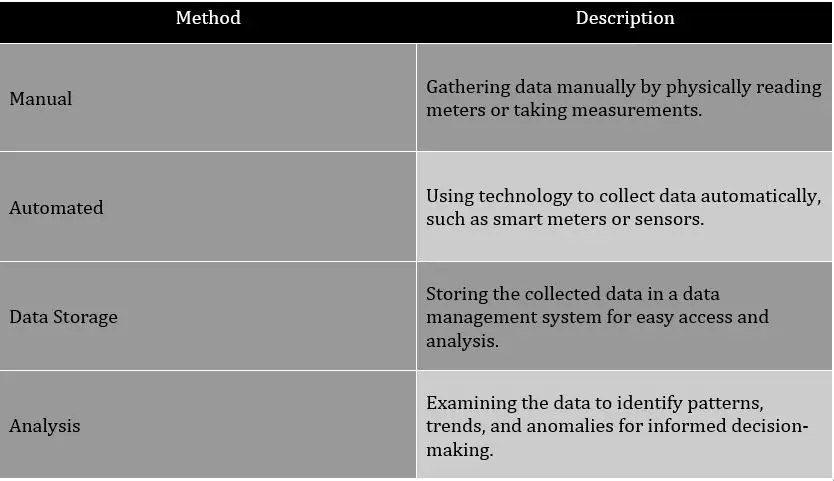
To collect and analyze utility data effectively, you must implement efficient methods and tools. These methods and tools allow you to gather and interpret the data accurately, giving you valuable insights into your infrastructure. One of the key tools you can use is a data management system. This system helps you organize and store the data in a structured manner, making it easier to access and analyze. Additionally, utilizing data collection devices such as smart meters or sensors can provide real-time data, giving you a more accurate and up-to-date picture of your utility usage.

Analyzing utility data involves examining the collected data to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies. This analysis can help you make informed decisions about infrastructure maintenance, energy conservation, and cost optimization. By understanding your utility data, you can identify areas for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and even predict future utility needs.
To illustrate the process of collecting and analyzing utility data, consider the following table:
Challenges in Managing Utility Data
When managing utility data, you may encounter various challenges that can impact the efficiency and accuracy of data collection and analysis. One of the main challenges is the lack of standardization in data formats and structures. Utility data can come from various sources, such as meters, sensors, and monitoring devices, and each source may have its own unique data format. This can make it difficult to integrate and analyze the data effectively.
Another challenge is the sheer volume of data that utility companies have to deal with. Utilities generate a massive amount of data on a daily basis, and managing and storing this data can be a daunting task. It requires robust data management systems and infrastructure that can handle large data sets and ensure data integrity.
Additionally, data quality can be a significant challenge in managing utility data. Errors in data collection, such as meter reading mistakes or sensor malfunctions, can lead to inaccurate data that can impact decision-making and analysis. Ensuring data accuracy and reliability requires implementing quality control measures and conducting regular data validation checks.
Lastly, privacy and security concerns also pose challenges in managing utility data. Utility data often contains sensitive information, such as customer usage patterns and billing details. Protecting this data from unauthorized access and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations is crucial for maintaining customer trust and data integrity.
Future Trends in Infrastructure Information
As we look ahead, you can expect to see exciting advancements in infrastructure information. The future holds great promise for the field, with emerging trends that will revolutionize the way we manage and utilize utility data. One such trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms into infrastructure information systems. These technologies will enable more efficient data analysis and decision-making processes, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimization of utility networks. Imagine a system that can predict and prevent infrastructure failures before they even occur, saving both time and resources.
Another trend on the horizon is the widespread adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in infrastructure management. These devices will enable real-time monitoring of utility assets, providing valuable insights into their performance and condition. With IoT, you can expect to see enhanced asset management, improved operational efficiency, and better customer service in the utilities sector.
Furthermore, there is a growing focus on data interoperability and standardization. As different utility systems become more interconnected, it is crucial to have a common language and framework for exchanging and integrating data. This will facilitate seamless communication between different stakeholders and enable more comprehensive analysis and planning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding utility data is crucial for managing infrastructure effectively. By collecting and analyzing this information, organizations can make informed decisions to improve efficiency and reliability. However, managing utility data can be challenging due to the complexity and volume of information. As future trends in infrastructure information emerge, it is important to stay updated and adapt to new technologies and techniques. Remember, staying proactive in utility data management will lead to better infrastructure outcomes.










