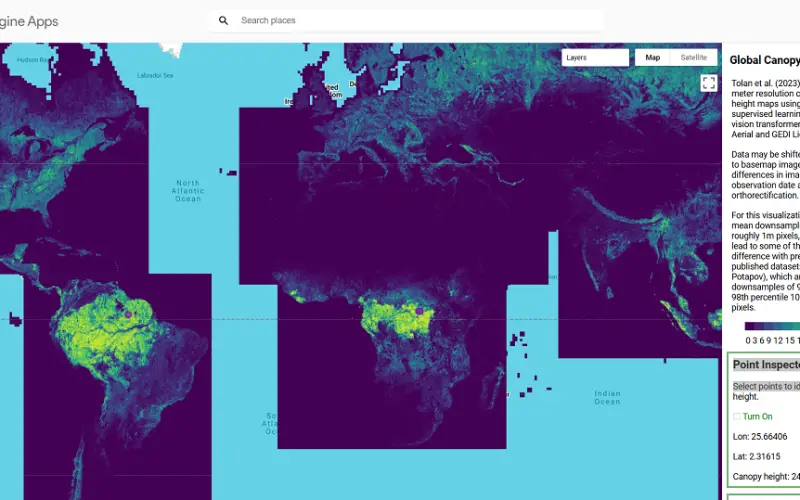
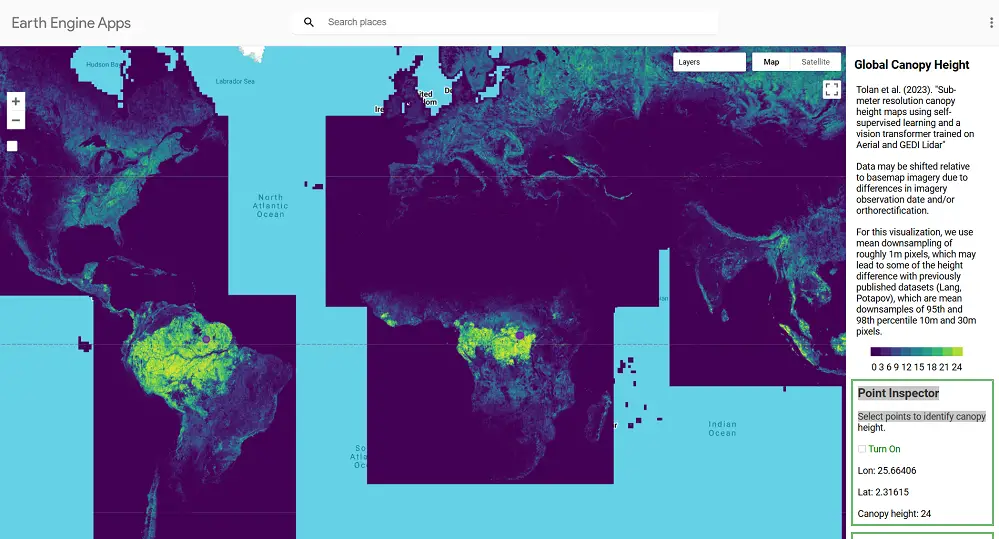
Meta, in collaboration with the World Resources Institute (WRI), has launched an advanced AI-powered Tree Canopy Map that provides unparalleled accuracy and detail in monitoring forests worldwide. By analyzing trillions of pixels across millions of satellite images, this map sets a new standard for forest data, enabling better conservation and more credible forest carbon credit systems.
Technology Behind the Map
At the heart of this initiative is Meta’s state-of-the-art AI model, DiNOv2, which processes over a trillion pixels from 18 million satellite images. The result is a highly accurate global dataset with a mean absolute error of just 2.8 meters. This level of precision is crucial for monitoring and verification, especially in areas where accurate data was historically hard to obtain.
The Tree Canopy Map employs advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze satellite imagery, identifying canopy heights with unparalleled accuracy. Unlike traditional methods, this AI-driven approach detects even the smallest details of tree coverage and integrates publicly available data, such as imagery from NASA and ESA satellites.
The dataset reveals groundbreaking insights, such as:
- Baseline Canopy Heights: Approximately one-third of Earth’s landmass—about 50 million square kilometres—has a canopy height exceeding 1 meter.
- Global Coverage: The map provides comprehensive monitoring of forests, including regions that were previously underrepresented in global datasets.
By establishing a global baseline for canopy height, the Tree Canopy Map offers essential information for understanding and managing forest ecosystems.
Significance of Forest Carbon Credits
Forest carbon credits are integral to combating climate change, allowing organizations to offset emissions by investing in forest conservation. However, the credibility of these credits depends heavily on reliable data.
The AI-powered Tree Canopy Map addresses this challenge by delivering precise tree canopy density and height measurements. Such accuracy strengthens carbon credit verification, ensuring that verifiable data back offsets. It also enables the identification of regions with high carbon sequestration potential, enhancing the credibility and impact of forest carbon markets.
This tool supports global efforts to meet climate goals, including targets under the Paris Accord. By quantifying carbon storage potential more effectively, the map helps evaluate conservation projects’ impacts and ensures data-driven decision-making in climate mitigation efforts.
Also Read – How Forest Mapping in Japan Enhances Carbon Sequestration
Open Access: A Commitment to Collaboration
A notable feature of this initiative is its commitment to open access. The map and associated datasets are freely available on platforms like AWS, Google Earth Engine, and GitHub. This open-access approach promotes collaboration and innovation, empowering researchers, policymakers, and businesses worldwide to leverage the data for various applications, including environmental monitoring and carbon credit verification.
Applications and Implications
The Tree Canopy Map is a transformative tool for conservation and forest management. It allows stakeholders to:
- Detect deforestation trends in near real-time.
- Plan reforestation efforts based on accurate canopy data.
- Quantify the carbon sequestration potential of forests with precision.
Moreover, this initiative exemplifies how artificial intelligence can address environmental challenges. Bridging gaps in data reliability and accessibility empowers global stakeholders to act effectively against deforestation.
Looking Ahead
Meta and WRI’s global Tree Canopy Map represents a pivotal advancement in leveraging AI for environmental conservation. Its accuracy, open access, and global reach set a benchmark for future innovations in sustainable forestry and carbon credit systems.
As technology continues to evolve, this tool will remain a cornerstone for effective forest management and climate action strategies. By providing reliable and accessible data, it fosters collaboration and innovation, ensuring a sustainable future for forests worldwide.
Source: Carbon Credits