Submitted By:

The term Digital Elevation Model (DEM), Digital Terrain Model (DTM) and Digital Surface Model (DSM) has several meanings and are not always understood properly, correctly or misinterpreted.
In this article I am trying to provide a clear understanding about DEM, DTM and DSM. Down the line you fill find out what is DEM, DTM and DSM and difference among DEM, DTM and DSM.
Let’s start to clear all the mist.
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
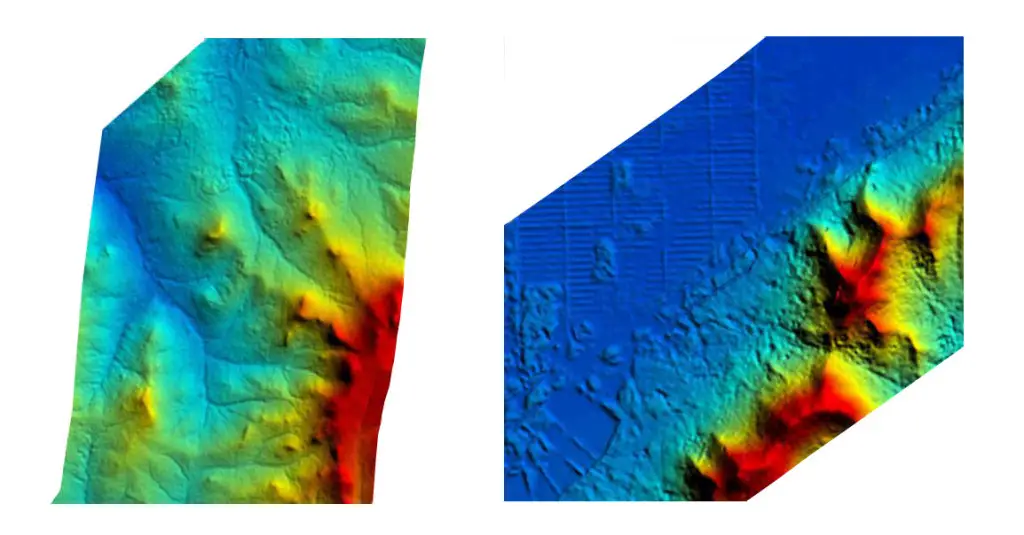
Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) are a type of raster GIS layer. In a DEM, each cell of raster GIS layer has a value corresponding to its elevation (z-values at regularly spaced intervals). DEM data files contain the elevation of the terrain over a specified area, usually at a fixed grid interval over the “Bare Earth”. The intervals between each of the grid points will always be referenced to some geographical coordinate system (latitude and longitude or UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator) coordinate systems (Easting and Northing). For more detailed the information in DEM data file, it is necessary that grid points are closer together. The details of the peaks and valleys in the terrain will be better modeled with small grid spacing than when the grid intervals are very large.

In short: DEM is used to refer specifically to a raster or regular grid of spot heights.
There is a variety of DEM source data available for developed areas and the suitability of this available data is depending on the project specifications. In remote regions around the World, were little or no source Data is available, the DEM can be produced by automatic DEM extraction from stereo satellite scenes, from Satellite sensors such as IKONOS (2-5m resolution), SPOT-5 (5-10m res.) and ASTER (15-25m res.).
Input to generate DEM
Following are the input source to generate DEM.
- Ground Control Points (GCPs).
- Contours.
- Triangulate Irregular Network (TIN).
- The DEM can also be provided from Stereo digital aerial photography at various resolutions, depending on the quality and scale of the aerial photography.
Types of DEM
A DEM can be represented as a raster (a grid of squares, also known as a heightmap when representing elevation) or as a vector-based triangular irregular network (TIN).

Heightmap of Earth’s surface (including water and ice) in equirectangular projection, normalized as 8-bit grayscale, where lighter values indicate higher elevation.
Source: Wikipedia
Digital Terrain Model
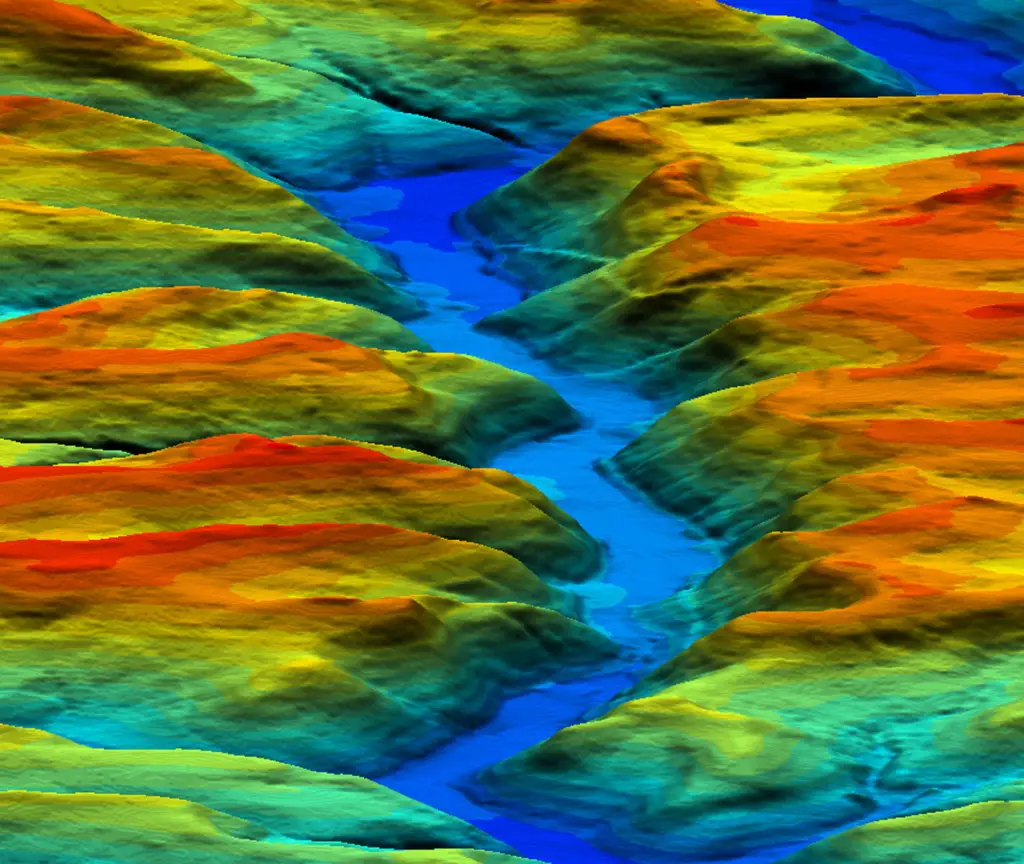
A digital terrain model (DTM) can be described as a three – dimensional representation of a terrain surface consisting of X, Y, Z coordinates stored in digital form. It includes not only heights and elevations but other geographical elements and natural features such as rivers, ridge lines, etc. A DTM is effectively a DEM that has been augmented by elements such as breaklines and observationsother than the original data to correct for artifacts produced by using only the original data. With the increasing use of computers in engineering and the development of fast three-dimensional computer graphics the DTM is becoming a powerful tool for a great number of applications in the earth and the engineering sciences.
For practical purpose this “Bare Earth” DEM is generally synonymous with a Digital Terrain Model (DTM).
DEM is far cheaper to produce an a DTM.
Quality and Accuracy of DEM/DTM
The quality of a DEM/DTM is a measure of how accurate elevation is at each pixel (absolute accuracy) and how accurately is the morphology presented (relative accuracy). Several factors play an important role for quality of DEM-derived products:
- terrain roughness;
- sampling density (elevation data collection method);
- grid resolution or pixel size;
- interpolation algorithm;
- vertical resolution;
- terrain analysis algorithm;
- Reference 3D products include quality masks that give information on the coastline, lake, snow, clouds, correlation etc.
Common uses of DEMs
- Extracting terrain parameters.
- Modeling water flow or mass movement (for example, landslides).
- Creation of relief maps.
- Rendering of 3D visualizations
- Creation of physical models (including raised-relief maps).
- Rectification of aerial photography or satellite imagery.
- Reduction (terrain correction) of gravity measurements (gravimetry, physical geodesy).
- Terrain analyses in geomorphology and physical geography.
Now let’s a have a look what is Digital Surface Model (DSM).
Digital Surface Model (DSM)
Digital Surface Model (DSM) represents the MSL elevations of the reflective surfaces of trees, buildings, and other features elevated above the “Bare Earth”.
In short: digital surface model represents the earth’s surface and includes all objects on it.
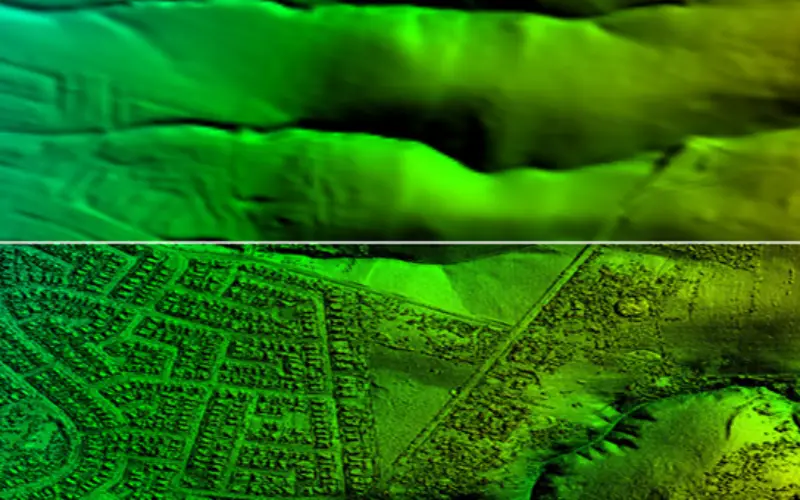
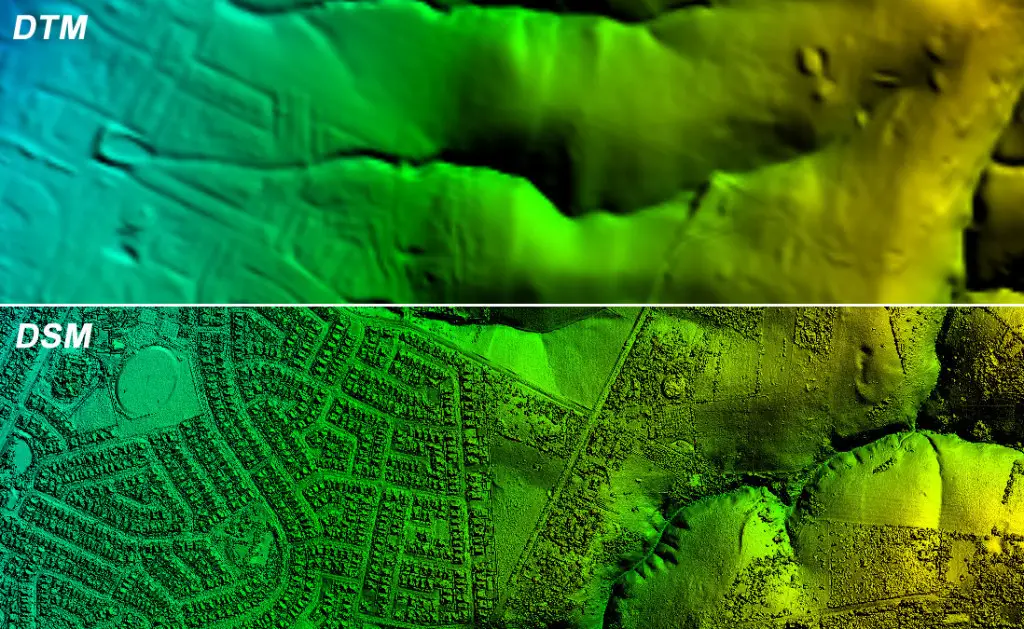
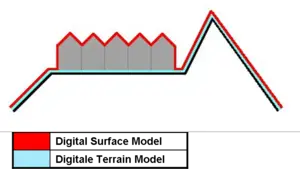
How DEM/DTM is Different from DSM
Now I am leaving on you to check out the difference between DTM/DEM and DSM. Given below are two figures to help you out.
Hope you might have understand the differences.
Enjoy :)














I tend to disagree on the differentiation between DEM and DTM stated above. Note that the surface “Elevation” and “Terrain” should be differentiated as one is focusing on the elevation modeling while the other one is on the terrain modeling.
Mr. Noordin Ahmad
Thanks for valuable comment; I would like to add a little more to your comment:
“DEM is an elevation model, which represent only heights of bare earth from a reference surface (vertical datum) mostly mean sea level”, where as a DTM is a terrain model which represents the characteristics of DEM and in addition other geographical elements and natural features such as rivers, ridge lines, etc.
“(DSM) represents the MSL elevations of the reflective surfaces of trees, buildings, and other features..”.. I see that nothing to deal with MSL of features..!!, but we can say its the exact height of specific features in 3D model..Any opinion about this kindly.
Mr. Omar
DSM represent the height of all the features (in case of tree, it is tree canopy) on the surface of earth with respect to a reference surface (MSL). In case of we are standing on ground and talking about the height of tree then it will have a different meaning.

If you something to say about this please let me know.
Following is the link to create DSM in ArcGIS.
http://resources.arcgis.com/en/help/main/10.1/index.html#//015w0000004q000000
Its very informative, to know about the DSM, DTM and DEM. it is really a good approach to understand it,
verry nice
That was good! I am more informed now than before.
It is good way of treating their difference
Very well explained… thanks a lot.. it helped me a lot in my presentation
I was confused, it s clear for me now. Thank you
Appreciating your work but need more clarifications and clear cut differentiating points
DTM represent (x,y,z) this is meaning represents dimensions are vertical and horizontal for surface earth . DEM represent (z) this is represents dimension is vertical only.
It’s cool that digital terrain models show the true shape of the earth without buildings. My uncle is in construction, so he may be interesting in reading this article. What are the benefits of both DTM and DEM surveys?
Then what is DTEM
Thank you all for your contributions, i will like to be clarify on something, DEM is a subset of DTM or it is the reverse please?
Subset may not be the right word. DTM is an improvised version of DEM with breaklines etc.
Hi There,
How can I modelling change between two DEM images. especially Geomorphology.
thanks alot I love this
Have a nice day!
Can you help? I’m looking for a LIDAR map of Hungary. Western Hungary.
Where can I find it? Is there at all? Thanks for the reply! Imre Mák from Hungary
Why elevation from DEM is higher than DSM? It should be lower????
Get the Elevation of a Location
This feature provides the altitude of a place from a geographic coordinate (latitude / longitude) in decimal degrees. The following URL is a request for the atitude of the place located at coordinate 45°30’N, 71°30’W for the CDEM coverage.
http://geogratis.gc.ca/services/elevation/cdem/altitude?lat=45.5&lon=-71.5
{
“altitude”: 326.0,
“vertex”: true,
“geometry”: {“type”:”Point”,”coordinates”:[-71.5,45.5]}
}
The equivalent URL for the altitude of the same place according to the CDSM coverage is:
http://geogratis.gc.ca/services/elevation/cdsm/altitude?lat=45.5&lon=-71.5
{
“altitude”: 320.919,
“vertex”: true,
“geometry”: {“type”:”Point”,”coordinates”:[-71.5,45.5]}
}
Each data product (DEM/DTM/DSM) delivers different elevation values as each model to create/produce these products may have used different methodologies & data source.
what is a difference between DTM and 3DM
Please refer to a scientific publication that is focussed on DEM terminology
A DEM is the more general “grouping” of either DSM or DTM.
A DTM is a DEM but also a DSM is a DEM.
But a DEM can be both DSM or DTM
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/13/18/3581