Accurate forest information is crucial for effective climate change strategies. Forests, covering about a third of the Earth’s land area, play a pivotal role in carbon sequestration—absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. In Japan, where forests cover 67% of the land, the challenge has been to collect detailed, precise data. Utilizing advanced technology, forest mapping in Japan is stepping up to maximize climate mitigation.
High-Precision Mapping for Effective Carbon Sequestration
Japan’s public and private sectors are collaborating to create high-resolution forest maps. Projects like the J-Credit Scheme certify carbon absorption from sustainable forest management, supporting the country’s climate goals.
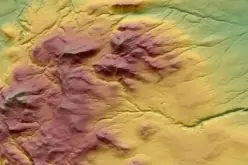
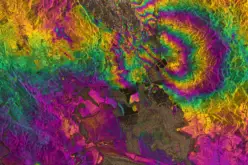
Recent technological advancements, including LiDAR and satellite data, have significantly improved mapping accuracy. For example, the University of Tokyo released a high-resolution forest map in 2024, revealing previously underestimated carbon stocks.
This emphasizes the importance of precise data for effective carbon capture strategies, underscoring the impact of forest mapping in Japan.
Also Read – Japan’s AI-Powered Navigation Aims to Save Lives from Wrong-Way Drivers
Using Technology to Measure Forest Ecosystems
Accurate data collection is not limited to tree count and age. Factors like tree species, forest health, and animal impact affect carbon absorption rates.
A study by Kyushu University found that excessive deer populations can reduce a forest’s carbon storage by half. Addressing this, an industry-academia project is using Yamaha Motor’s LiDAR technology mounted on unmanned helicopters to measure not only trees but the entire forest ecosystem.
This initiative is a key part of forest mapping in Japan, improving the understanding of biodiversity’s role in carbon absorption.
Open-Source Data for Broader Climate Action
One of Japan’s most significant steps in climate action is making forest data open-source. Historically, forest data was limited to forestry experts and specific organizations. Now, by digitizing and sharing this information, a broader range of stakeholders, from local governments to private businesses, can access it.
This data-driven approach allows for targeted management strategies tailored to specific forest conditions, maximizing carbon sequestration and reducing emissions effectively. This open-source effort is central to the goals of forest mapping.
Conclusion: Japan’s Commitment to Climate Change Mitigation
Japan’s leadership in detailed forest data mapping not only supports domestic climate strategies but also aligns with global goals, such as those outlined in the Paris Agreement.
The country’s innovative use of technology, combined with open-source data sharing, enables more accurate forest management and enhances its ability to capture carbon.
Forest mapping in Japan continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in forest conservation, setting a strong example for other nations in the fight against global carbon emissions.
Source: World Economic Forum