Tamil Nadu Uses GIS to Protect Ramsar Sites
Tamil Nadu is embracing advanced technology to safeguard its Ramsar sites, wetlands of global ecological importance. The Tamil Nadu Wetland Authority plans to utilize drones, machine learning, and GIS to protect Ramsar sites from degradation. This innovative approach aims to ensure the long-term sustainability of these critical ecosystems.
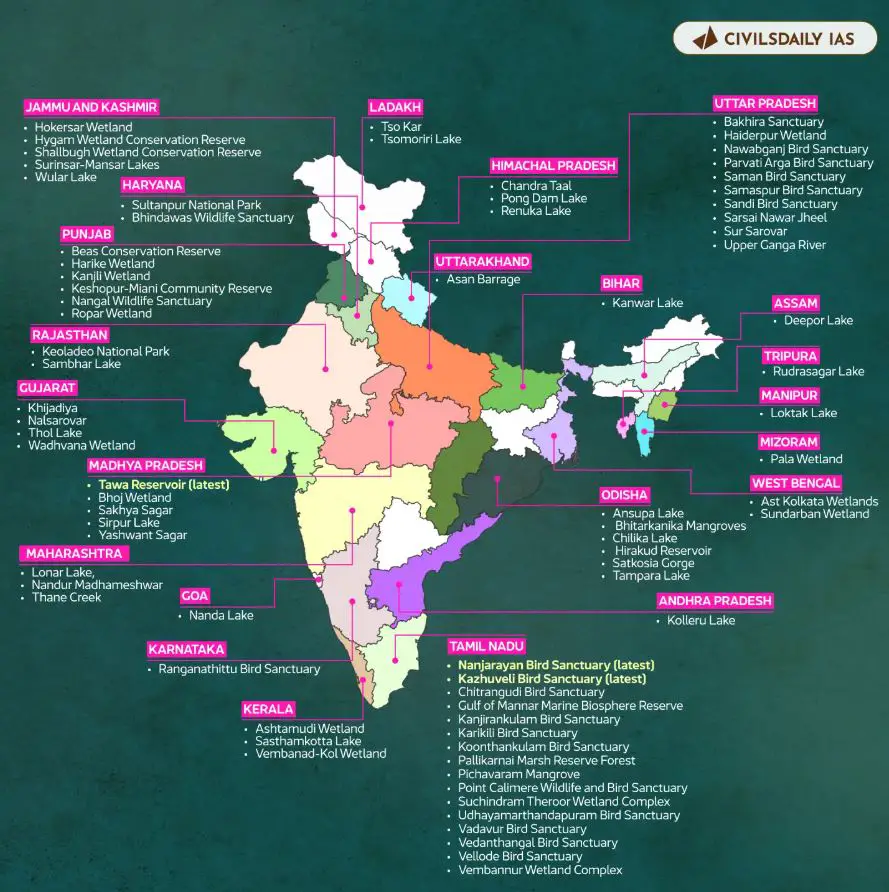
Ramsar Sites in Tamil Nadu
The state is home to 14 Ramsar sites, contributing significantly to India’s wetland wealth. Notable locations include the Pichavaram Mangroves, Pallikaranai Marshland, and Point Calimere Wildlife Sanctuary. These wetlands support biodiversity, regulate water cycles, and act as natural buffers against climate change. Efforts using GIS to protect Ramsar sites will provide actionable insights into their health and vulnerabilities.
Role of Advanced Technology
The project involves drone mapping to perform aerial surveys of wetlands, offering detailed visuals and data. GIS technology combined with machine learning will analyze spatial changes over time, identifying threats such as encroachments and pollution. By integrating these technologies, the Wetland Authority aims to create a dynamic database for monitoring and conservation planning.
Why Ramsar Sites Matter
Ramsar sites are vital for global biodiversity and ecosystem services. They provide habitat for migratory birds, support local livelihoods, and help mitigate climate risks. For instance, the Chilika Lake in Odisha and Tamil Nadu’s Pallikaranai Marshland highlight their ecological and economic importance. By using GIS to protect Ramsar sites, Tamil Nadu sets an example for other regions in sustainable wetland management.
Moving Ahead
This initiative aligns with the Ramsar Convention’s goal of promoting the wise use of wetlands. Tamil Nadu’s focus on using GIS to protect Ramsar sites underscores the importance of technology-driven conservation efforts. Collaboration with local stakeholders and experts will further enhance the success of this project, ensuring these natural treasures remain intact for future generations.
By prioritizing technology and sustainability, Tamil Nadu is paving the way for efficient conservation practices, securing the ecological and economic value of its wetlands.
Sources: