Most national security decisions involve geography. Whether assessing potential terrorist targets, planning where to strike on the battlefield, or deciding where to locate a new building with minimal environmental impact, geography always comes into the equation.
Geographic Information System (GIS) play a pivotal role in Military operations as they are essentially spatial in nature The concept of Command, Control, Communication and Coordination in military operations are largely dependent on the availability of accurate information in order to arrive at quick decisions for operational orders. In the present digital era, GIS is an excellent tool for Military commanders in the operations.
GIS is Revolutionizing defense strategy and intelligence operations, providing unparalleled capabilities for data analysis, visualization, and decision-making. As global security threats become increasingly complex, the integration of GIS technology offers military and intelligence agencies a powerful tool to enhance situational awareness, streamline operations, and improve strategic planning. From real-time battlefield mapping to sophisticated intelligence gathering, GIS is revolutionizing the way defense strategies are conceived and executed, ensuring that forces remain agile, informed, and ready to respond to emerging threats.
This article explores the multifaceted impact of GIS on modern defense and intelligence operations, highlighting key innovations and real-world applications that underscore its critical role in maintaining national and global security.
GIS technology is rapidly moving from its historic niche usage within defense to becoming a critical defense wide infrastructure. The assessment is based on the fact that defense operations of all kinds depend on a sound understanding of terrain or geography. This involves more than an understanding of location—geography is a science that creates a framework for understanding the relationships between all entities in an area of interest. This, in turn, fosters the development of spatial knowledge from the flood of data. The creation of a spatial infrastructure also leads to the sharing of data and applications throughout the networked environment. GIS is now widely used throughout the warfi ghter, business, and strategic intelligence domains.
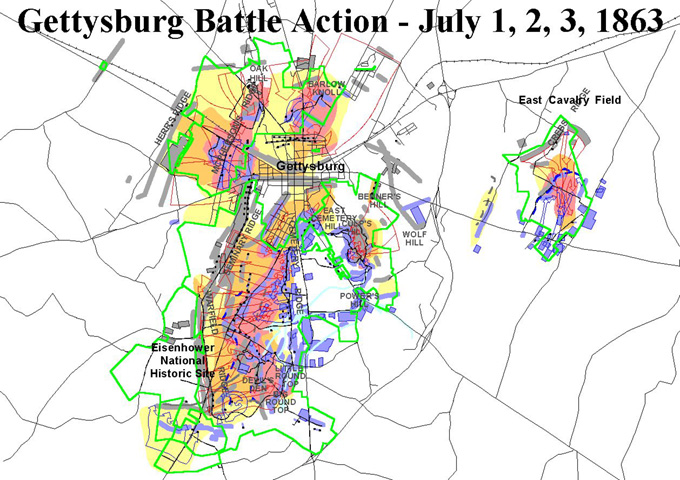
The focus on military efforts continues to be a major force with a heavy reliance on technology. Technology has not only changed the way wars are fought but its employment has become a key factor in attaining dominance in military power. The battle victory is complete only after ground forces occupy the enemy land and take control of the area. To hold and maintain the control of the occupied land, armed forces need to know the spatial extent upon which they have the control.
The need to swift and accuracy information was amply demonstrated during the Gulf war by Allied forces against Iraq. In an article published in Electronic Today (November 1996), Major General Gurbaksh Singh VSM, states:
“The lessons gained from military history indicate that the key to military victory lies (regardless of military size of the opposing forces) in remaining ahead of the enemy in time sensitive SCORE loop of C4I2 process.If a defending force or weapon system can with some accuracy and sufficient warning finds out where the attacker is or his future course of action would be, it would be easier to defeat him by occupying position of advantage or by massing a superior force at the point of decision.”
This statement reinforces how important spatial information is to field commanders for determining the best decision for military operations. “C4I2″ in Major General Singh’s statement refers to Command, Control, Communication, Coordination, Information and Interoperability. He has rightly indicated the importance of Interoperability, which is very important aspect in the current scenario of proliferation of several computer systems and software systems used in the military operations.
What we do with GIS ?
Command and Control
Spatial data is of crucial importance to the Military Commander in the battle as it is for a decision maker in planning and development in a state’s growth. Ministry of Defense (MOD) in any country gathers data on routing, filtering, analyzing and presenting information for decision-making. The regional conflicts, rapid deployment and flexible response imposes heavy burden on military commanders, their staff and supporting system to keep up-to-date situation on the ground about enemy activities. Visualizing raw tabular data within a spatial framework has many benefits. Therefore digital mapping and Geographic Information System (GIS) occupy center stage in activities as diverse as battlefield simulation, mission briefing and communications planning, logistics management and command control.
Defense Estate Management
The value of this GIS technology as an administrative support is significant, particularly; the MOD holds large chunks of property across the nation. Use of GIS in the management of military bases facilitates maintenance and the tackling of all stores, which may be found on the base. “GIS allows military land and facilities managers to reduce base operation and maintenance costs, improve mission effectiveness, provide rapid modelling capabilities for analyzing alternative strategies, improve communication and to store institutional knowledge.”
Terrain Evaluation
In land based military operations Military field commanders would like to know terrain conditions, elevations for maneuvering armour carriers, tanks and for use of various weapons. In addition, they need vegetation cover, road networks, and communication lines with pin pointing accuracy for optimizing the resource utilization. A detailed land map with information on the land use, terrain model and proximity of habitat are essential for military operations. All these details must be available to the field commanders on a datum to match with the equipment he uses for position fixing and communication in his area of operation. Any discrepancy in these inputs may endanger the operation. Target assessment can only be done if the inputs are properly matching with the system used for firing the weapon.
Viewing Spatial Data
Most potential users of GIS are viewers. There are personnel right from field commanders to command staff. They need access to a geographic picture, map or photograph to help and assess a situation to carry out planned operations.
Naval Operations
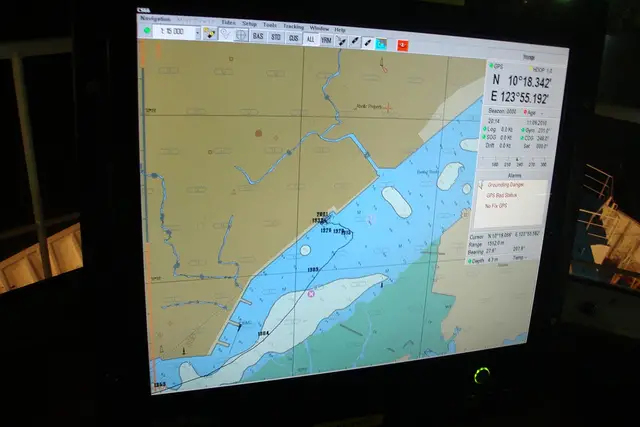
At sea Naval vessels depend largely on indirect methods to navigate when there is no means of establishing their position with visual aids. Global Positioning System (GPS) provides the means of determining the position at sea. Naval vessels will be operating at sea using several electronic gadgets for operations. Recent technological advances have provided the means to assess the unknown to greater accuracy.
The recent induction of Electronic Chart Display and Information System (ECDIS), on the bridge of the vessels, helps the navigator to navigate the ship safely in all weather conditions. Electronic Navigation Chart (ENC) is a replacement of conventional paper chart, which is used as tool for navigation, provides inputs for detailed information about depth, hazards and navigational aids within the area. This supported by visual and audio alarms of ECDIS provide the navigator, sufficient means to navigate the vessel safely. The display is used to provide selective spatial or textual information to the navigator for safe passage. ENC is the database for GIS operations and ECDIS is the real time GIS application in marine environment.
In addition, ECDIS can be used to other naval operations using additional layers of information related to oceanographic and meteorological conditions to provide the means for naval operations such as anti-submarine or beach landing of armed forces in military operations. NATO is standardizing additional Military layers to be used for operations using ENC database as base data in conjunction with shipboard ECDIS system.
Air Operations
Air operations in battle environment require the similar inputs as per land operations along with precise height information for targeting. These include the detailed information about the target location, proximity of civilian areas, and terrain evaluation and meteorological conditions besides navigational data. The virtual reality concepts are of greater help in fighter and bombing aircrafts for effective air strike operations.
Military leaders heavily depend on GIS and GPS (Global Positioning Systems) to make tactical decisions such guiding troops, supplies/equipment and ships, informing them of possible threats, problems with terrain in which they will encounter and also to direct their attention to specific areas of interests.
Weather Information
Weather plays dominant role in the battlefield. Real time weather information is essential for field commanders either on land or in sea or in air for successful completion of the task. At times, weather may play crucial role in success or failure of an operation. Every battlefield commander would like to know the information regarding cloud coverage, wind conditions, visibility, temperature parameters and other related inputs.
GIS System
The computer based Geographical Information Systems can provide automated assistance to military forces terrain analysis function. However these software systems and utilities have limitations, as they are not full-featured GIS. The greatest limitation is the users ingenuity and the data, which is used. These systems have the capability to receive, reformat, create, store, retrieve, update, manipulate and condense digital terrain data to produce terrain analysis products such as: modified combined obstacle overlays, hydrology overlays, slope maps, on and off road mobility maps, line-of -sight plots, concealment maps and possible problems associated lines of communication.
Positional Information
One of the most important functions of GIS along with satellite imagery is to understand and interpret terrain, which is a major role in determining how troops can be deployed in the quickest and most effective way. Understanding the landscape is especially useful because a military leader can determine strategic positions, such as ideal locations for scouting parties, best line of sight/fire and also the ability to hide troops and equipment.
Logistics Management
GIS plays an important role military logistics because it helps in moving supplies, equipment, and troops where they are needed at the right time and place. By using GIS in determining routes for convoys, forces are able to determine alternative routes if mishaps or traffic jams occur on the most direct route. By using both GPS and GIS certain sensitive articles such as; nuclear warheads can be tracked every step of their shipment and also kept away from hot spots, populated areas or other shipments.
Defence Mapping
Military needs maps for different purposes within its operational command and each requirement is to cater for a specific purpose. The digital base in GIS environment facilitates the creation of different types of maps to meet specific user needs without clustering with unwanted details. This facilitates the viewing of spatial information on need to know basis either at command headquarters or in the field area. The battle commanders can evaluate thematic information for analyzing the real time scenario by manipulating the information available at their disposal.
Common Horizontal Datum
It is necessary that the spatial data for the use by Military units reside within framework of single Datum for coordinating joint service operations. There is a bottleneck in this aspect in the present scenario of military operations. Colonel Whittington of UK Military Survey at ESRI 1997 European User Conference amply explained this. According to him
” the maritime operators use a vertical datum based on the high water mark; the land operators use a vertical datum based on mean sea level, while the air operators are more concerned with the obstruction heights above ground level. The amphibious operators are not concerned about the use of Datum and they do not rely on computer”
This becomes more complex when multinational forces are deployed. This was evident in Bosnia conflict where there is difference in target position computed by European Datum and WGS84 by few hundred meters. Even a larger displacement was observed when local Yugoslavia datum was applied. In India, we use Everest Datum and use of GPS receivers in the field may pose problem unless the datum shift is correctly established.
All this brings down to the fact that a common datum is necessary and slowly WGS84 is emerging as a common datum for all such operations. The technological advances in position fixing using satellites is based on WGS84 and most of the civilian applications also need to be shifted to this datum in course of time. Military applications are no exception. However, this is a gigantic task and to achieve a common datum across the world needs money and expertise. Most of the countries may not have the resources in terms of funding and technology to handle this change.
As an interim measure, there should be at least interoperability between the three wings of Armed forces to use a common reference datum in their activities in mapping for effective conduct of joint military operations.
GIS technology helps armed forces as information is readily available to various levels of officers involved in operations. The advent of remote sensing technology has provided great Philip to intelligence units in defense forces to acquire data on enemy activities from eyes in the sky. Spy satellites constantly acquire the high-resolution satellite data in peacetime to monitor the development in acquisition of modern warfare gadgets by the enemy forces. There is no privacy as far as these satellites are concerned and the developed countries have been extensively using remote sensing techniques in monitoring the enemy activities in establishing nuclear installations. These are brought to the notice of International Agencies coordinating the prevention of use of nuclear energy for destructive purposes.
The use of remote sensing data combined with ground information would provide a common platform for analyzing the ground situation in time of war. The induction of satellites providing high-resolution images in the present era enhanced the ability of accurate map-making and by making the latest information available to the forces.
Source: ESRI, Filed in Geospatial World by Satyanarayana and Yogendran