IIT Bombay Unveils AMVG Model That Reads Satellite Images with Natural-Language Prompts
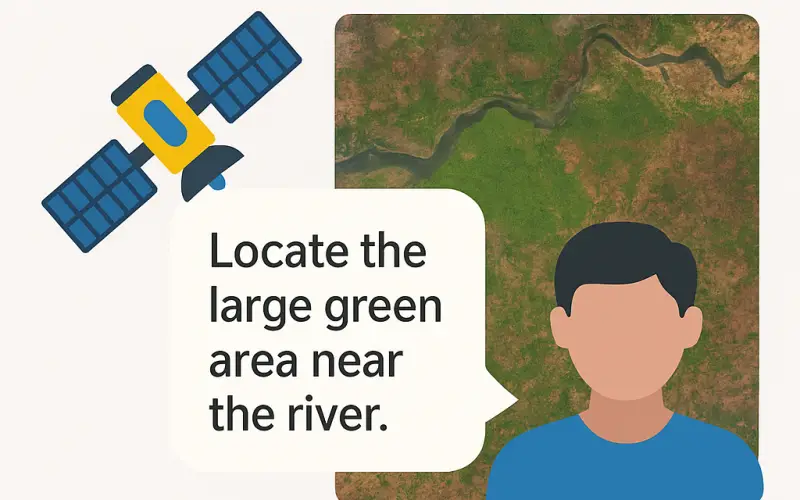
In a breakthrough for remote sensing technology, the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IIT Bombay) has developed the Adaptive Modality-guided Visual Grounding (AMVG) model, capable of interpreting satellite and aerial imagery using natural, often ambiguous, human-language prompts. The model was unveiled in a study published in ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing and released under an open-source license to promote broad scientific access and innovation.
Experience & Expertise
IIT Bombay’s researchers, led by PhD scholar Shabnam Choudhury, bring deep expertise in visual grounding and remote sensing. Shabnam explains that conventional visual grounding models struggle with ambiguous language and complex satellite imagery. AMVG model addresses these challenges head-on, establishing an industry-leading standard in multimodal AI integration.
Innovations & Authoritativeness
What sets AMVG model apart are four key innovations:
- Multi-modal Deformable Attention layer
- Multi-stage Tokenised Encoder (MTE)
- Multi-modal Conditional Decoder
- Attention Alignment Loss (AAL), which “nudges” the model when its attention drifts off-target.
Together, these innovations give AMVG the ability to parse cluttered, noisy, and scale-variant satellite imagery more accurately than previous models. This development strengthens IIT Bombay’s reputation as a trusted authority in AI-driven Earth-observation research.
Also Read – Unlocking Resources with Remote Sensing Mineral Detection
Real-World, Trustworthy Impact
AMVG holds real-world potential across multiple critical domains:
- Disaster response, by rapidly identifying features such as flood zones or collapsed structures from satellite imagery.
- Urban planning, by deciphering infrastructure from varied-angle images.
- Agricultural productivity, through precise land-use mapping.
To reinforce trust and reproducibility, IIT Bombay has open-sourced the entire AMVG framework via GitHub—reflecting a commitment to transparent, collaborative research. Still, researchers caution that AMVG’s performance varies across unseen sensors or regions, and further optimization is needed for real-time or edge-device deployment.
Open-Source and Future Outlook
In keeping with IIT Bombay’s focus on research transparency, the team has released AMVG model as open-source software on GitHub. This move allows scientists, developers, and policymakers worldwide to test, validate, and extend the tool.
However, researchers acknowledge challenges remain. The model still requires optimization for different satellite sensors and geographic contexts. Running it on edge devices for real-time analysis also demands further innovation.
A Step Toward Human-Centric AI
The launch of AMVG model demonstrates IIT Bombay’s leadership in artificial intelligence for geospatial research. By combining human-like language processing with high-resolution imagery, the tool opens up possibilities for smarter, faster, and more inclusive decision-making.
As global demand for Earth observation grows, tools like AMVG model may soon become essential for understanding our planet’s rapidly changing landscapes.