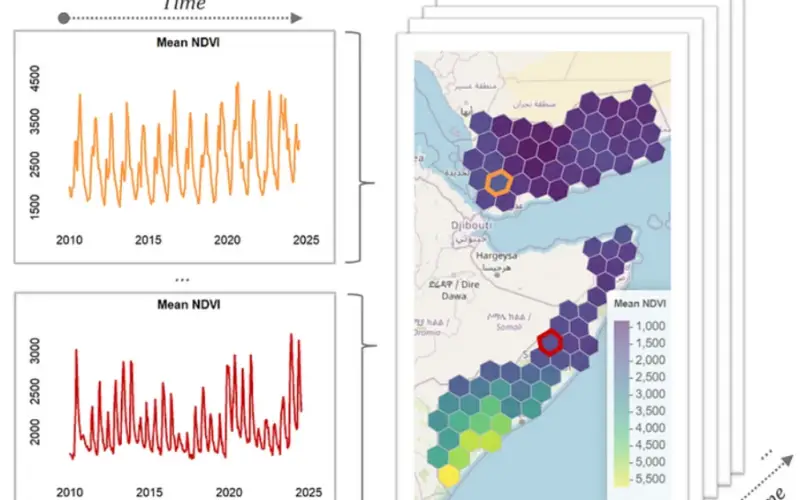
A new R package called geeLite is helping bridge the gap between massive satellite datasets and local-level decision-making. Developed through a collaboration between the World Bank and University College London, geeLite offers a simplified way to manage and update geospatial databases using Google Earth Engine (GEE), making remote sensing data more accessible than ever.
Researchers, NGOs, and policymakers often face technical roadblocks when trying to access and work with satellite-derived data. geeLite changes that. It enables users to extract, store, and analyze data—such as vegetation, rainfall, or land surface temperature—without writing complex code or maintaining cloud servers. The tool supports both small- and large-scale projects through two processing modes: “local” for quick tasks and “drive” for more extensive jobs using Google Drive as an intermediary.
The heart of geeLite lies in its automation and flexibility. Users can define a simple configuration file to specify regions, variables, and timeframes. The package then performs the rest—downloading and storing the data into a lightweight SQLite database. These databases are easily portable and ideal for environments with limited internet connectivity.
Also Read – World Bank Tool Helps Map Solar Potential
A recent World Bank working paper praised geeLite for removing technical entry barriers and supporting reproducible workflows. The tool also makes use of Uber’s H3 hexagonal grid system, enabling efficient spatial aggregation across different resolutions. This helps researchers track indicators like vegetation health (NDVI), precipitation, and even drought conditions more accurately.
Importantly, geeLite allows databases to be updated automatically. With basic scheduling tools, users can keep their geospatial indicators current without manual effort—benefiting agriculture monitoring, climate adaptation planning, and disaster risk assessments.
Getting started with geeLite is straightforward. The package can be installed via GitHub, and users only need to authenticate with Google Earth Engine once. From there, a single function—run_geelite()—triggers the entire data ingestion process. Analysis and visualization can then be done in R with built-in helper functions.
By combining user-friendliness with powerful geospatial capabilities, geeLite empowers local actors to harness satellite data for timely, evidence-based decisions. As remote sensing continues to evolve, tools like geeLite ensure that insights don’t stay locked in the cloud—they reach the communities that need them most.
Source: Blogs.WorldBank