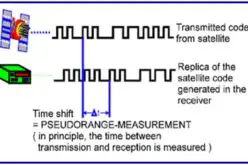
RINEX, or Receiver Independent Exchange Format, has been a cornerstone in the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) community since its inception. It allows the exchange of raw satellite navigation data between different receivers and software applications. Over the years, RINEX has evolved significantly, adapting to the growing needs and technological advancements in GNSS.
The latest version, RINEX 4.0, represents a significant leap forward in terms of features and capabilities. This article explores the journey of RINEX from its humble beginnings to the cutting-edge RINEX 4.0, with a specific focus on the recent update to RINEX 4.01.
Milestones in RINEX Versions
As GNSS technology advanced, so did the need for more sophisticated data formats. This led to the release of subsequent RINEX versions, each bringing significant improvements over its predecessors.
RINEX 2.x
RINEX 2.x, released in the early 1990s, introduced several enhancements over version 1.0. It added support for more satellite systems, including GLONASS, and improved the handling of multi-frequency data. This version also included more detailed metadata, which helped in better understanding and processing the GNSS data.
RINEX 2.x supported GPS and GLONASS observations, meteorological data, and navigation files. Additionally, the C2, L2C/L5, and Galileo codes were introduced, allowing for more comprehensive data collection and analysis.
Also Read – Comparative Study of Online GPS Post Processing Services and Effects on DGPS Data Processing
RINEX 3.x
The release of RINEX 3.x in 2007 marked a major milestone, introducing a flexible format to support future GNSS systems.
- RINEX 3.01: Added support for GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou (Compass), QZSS, and SBAS, with detailed signal generation.
- RINEX 3.02: Included a new header for GLONASS code-phase bias, mandatory GLONASS frequency-to-slot message, and a new naming convention.
- RINEX 3.03: Refined the format with updates to support evolving GNSS data needs.
- RINEX 3.04: Supported signals from GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, QZSS, and IRNSS, with updates for GLONASS CDMA and new BeiDou III/QZSS II signals, and improved readability.
- RINEX 3.05: Restructured for clarity, added BeiDou signals and tracking codes, and included missing flags in GLONASS navigation messages.
RINEX 4.0: The Cutting Edge
RINEX 4.0, the latest major version, represents a significant leap forward in GNSS data management. Released in 2020, RINEX 4.0 builds on the strengths of previous versions while introducing new features that address the latest advancements in GNSS technology.
- RINEX 4.0: Released in 2021, this major update modernized the Navigation message files to handle new data from all GNSS constellations, including ionospheric corrections and Earth orientation parameters. The Observation file format added new QZSS signals and tracking codes to support the upcoming L1 C/B signal. The Meteo file format stayed the same, and new optional header lines were added to support FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) data principles.
- RINEX 4.01: Released in 2022, This update introduced new observation codes for GPS on L1 and L2 to support future Block IIIF RMP signals. It also added L1 observation codes for the NavIC constellation and included various editorial improvements.
New Features in RINEX 4.0
- Enhanced Precision: RINEX 4.0 offers even higher precision by allowing for more significant digits in the recorded values, which is crucial for applications requiring centimetre-level accuracy.
- Extended Metadata: This version includes more detailed metadata, providing a better context for the GNSS data and improving the reliability of data processing.
- Support for New GNSS Signals: RINEX 4.0 supports the latest signals from all major GNSS systems, including new frequencies and modulation schemes.
- Improved Data Integrity: Enhanced error-checking mechanisms have been introduced to ensure the integrity and reliability of the recorded data.
- Backward Compatibility: Despite its new features, RINEX 4.0 maintains backward compatibility with previous versions, ensuring a smooth transition for users upgrading from older versions.
RINEX 4.01: The Latest Update
Following the release of RINEX 4.0, an update was made in 2021 with the release of RINEX 4.01. This update primarily focused on refining the features introduced in 4.0 and addressing minor issues identified by early adopters. Key improvements in RINEX 4.01 include:
- Enhanced Signal Support: Further improvements in handling new GNSS signals.
- Metadata Refinements: Additional metadata fields to support more detailed data analysis.
These refinements ensure that RINEX 4.01 is not only more reliable but also more versatile, solidifying its position as the cutting-edge standard for GNSS data exchange.
Comparison of Different RINEX Versions
Here’s a comparative table highlighting the evolution of RINEX features across different versions:
The Future of GNSS Data Exchange
The release of RINEX 4.0 and its subsequent update to 4.01 set the stage for future innovations in GNSS data exchange. As GNSS technology continues to evolve, the need for more sophisticated and versatile data formats will only grow. RINEX 4.0 and 4.01 address many of the current challenges in GNSS data management, but they also pave the way for future developments.
Potential future enhancements in RINEX may include support for even higher precision, integration with other geospatial data formats, and improved handling of multi-constellation and multi-frequency data. As the GNSS community continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, RINEX will remain a crucial tool in enabling and supporting these advancements.
Conclusion
The journey of RINEX from version 1.0 to 4.0, and the recent update to 4.01, is a testament to the rapid advancements in GNSS technology and the ongoing efforts to improve data exchange and interoperability.
RINEX 4.0, with its enhanced precision, extended metadata, and support for new GNSS signals, represents the cutting edge of GNSS data management. The refinements in RINEX 4.01 ensure that it remains a reliable and versatile standard for the GNSS community.
Read more about RINEX 4.0 Release notes on IGS.